The pond as an ecosystem
The pond as an ecosystem
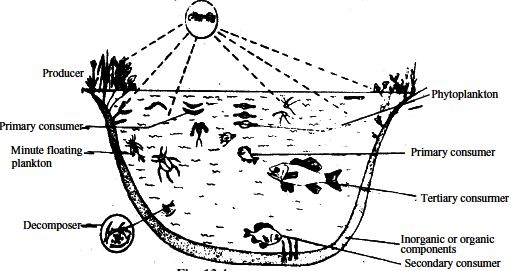
Pond is a small body of still freshwater formed naturally or by artificially where algae, aquatic plants, insects, fishes, and birds are live. The complex interactions between the biotic and abiotic components of pond form a self-sufficient and self-regulating system.The pond is the simplest aquatic ecosystem. Where Algae are eaten by microscopic animals, which are eaten by small fish on which larger carnivorous fish depend. These are in turn eaten by the aquatic birds. Aquatic insects, worms and snails feed on the waste material excreted by animals and the dead or decaying plant and animal of pond and break down into nutrients which aquatic plants can absorb, thus completing the nutrient cycle in the pond. Location, size, depth, water quality, pH of the water and several inorganic and organic substances of a pond influence the pond ecosystem.
 |
| pond ecosystem |
Structure of pond ecosystem –
Like every ecosystem, pond ecosystem also consists of two major component -
Abiotic component
Biotic componentAbiotic component –
abiotic component of pond ecosystem includes temperature, light, pH of the water and several basic inorganic substances like oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, phosphorous, Calcium, Sulphur and organic substances like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids etc., make the abiotic components.Biotic Components
Producers:
This category includes green plants which may be submerged, free-floating or amphibious.Example - Hydrilla, Ceratophyllum, Vallisneria, Jussiaea, Lemna, Eichornia, Salvinia, Spirogyra, Oedogonium, Chlamydomonas, Volvox, Anabaena etc.
Consumers:
(i) Primary Consumers:
Zooplanktons:
protozoans, rotifiers, Lecane, Crustaceans etc.
Benthos:
Larvae of insects, beetles, small fishes, mites, molluscs etc.(ii) Secondary consumers:
Insects, water beetles, frogs, fishes etc.
(iii) Tertiary Consumers:
Big fishes eating small fishes belong to this group.(c) Decomposers:
Several bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes represent this group.Example: Aspergillus, Saprolegnia, Fusarium, Rhizopus etc.



Comments
Post a Comment